Resistor : It is one kind of power which
prevents the flow of current.
A
resistor is one of the most fundamental components in electronics. Its purpose
is to impede a flow of current and impose a voltage reduction. It consists of
two wires or conductors attached at opposite ends or sides of a relatively poor
electrical conductor, the resistance of which is measured in ohms, universally
represented by the Greek omega symbol, Ω.
Example: The electronic component known
as the resistor is best described as electrical friction. Pretend, for a moment,
that electricity travels through hollow pipes like water. Assume two pipes are
filled with water and one pipe has very rough walls. It would be easy to say
that it is more difficult to push the water through the rough-walled pipe than
through a pipe with smooth walls. The pipe with rough walls could be described
as having more resistance to movement than the smooth one.
Electronic resistor .
How It Works
In the process of impeding the flow of current and reducing
voltage, a resistor absorbs electrical energy, which it must dissipate as heat.
In most modern electronic circuits, the heat dissipation is typically a
fraction of a watt. If R is the resistance in ohms, I is the current flowing through
the resistor in amperes, and V is the voltage drop imposed by the resistor (the
difference in electrical potential between the two contacts that are attached
to it), Ohm’s law states:
V = I / R
This
is another way of saying that a resistor of 1Ω will allow a current of 1 amp when the
potential difference
between the ends of the resistor is 1 volt. If W is the power in watts dissipated by the
resistor, in
a DC circuit:
W = V * I
By substitution in Ohm’s law, we can express watts in terms of
current and resistance:
W = I2 / R
We can also express watts in terms of voltage and resistance:
W = V2 * R
These alternates may be useful in situations where you do not know
the voltage drop or the current, respectively. Approximately similar
relationships exist when using alternating current, although the power will be
a more complex function.
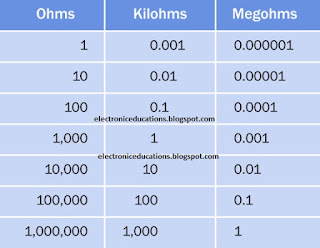
Values
1 kilohm, usually
written as 1K, is 1,000Ω. 1 megohm, usually written as 1M or 1 meg, is 1,000K. 1 gigaohm
is 1,000 megs, although
the unit is rarely used. Resistances of
less than 1Ω are uncommon and are usually expressed as a decimal number followed by the Ω symbol. The term milliohms
(thousandths of an ohm)
is used in special applications. Equivalent resistor values are shown in picture
.
Tolerance
The tolerance, or precision, of a resistor may range from
plus-or-minus 0.001% up to plus-orminus 20%, but is most commonly plus-or-minus
1%, 2%, 5%, or 10%.